A relational database stores data in multiple tables and connects them using defined relationships. Each table holds a specific type of data, and relationships link related records across tables.
This structure allows you to organize data clearly and use the same data across forms, workflows, views, and reports.
¶ 1. Relational database working model
In a relational database, data is stored in tables and connected using defined relationships. Each table represents one business entity. Each row represents one record. Each column represents one attribute of that record.
- Every table has a Primary Key. The primary key uniquely identifies each record in the table.
- A Foreign Key is a field in one table that refers to the primary key of another table. This is how tables are linked.
These links allow data to move across tables in a controlled and consistent way.
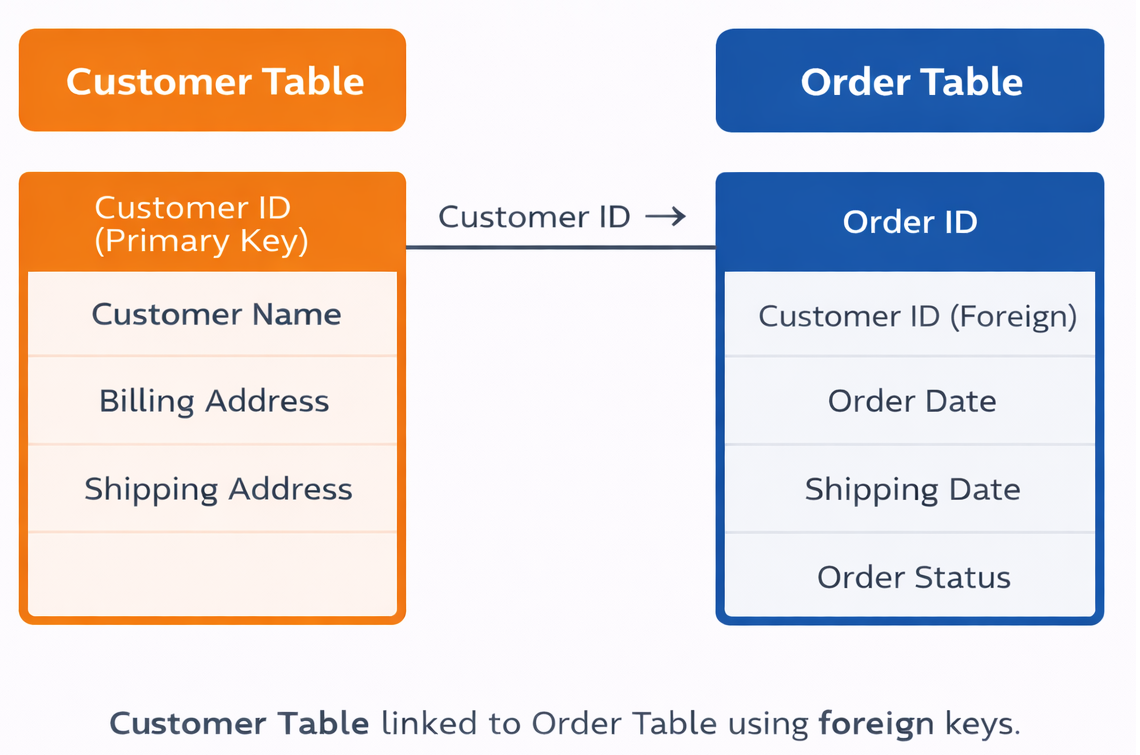
¶ Customer and Order Relationship
To understand how relationships work, consider two tables: Customer and Order.
| Customer Table | Fields |
| Contains customer information | Customer ID, Primary Key |
| Customer Name | |
| Billing Address | |
| Shipping Address |
Each customer has a unique Customer ID. This ID identifies the customer across the system.
| Order Table | Fields |
| Contains order information | Order ID, Primary Key |
| Customer ID, Foreign Key | |
| Order Date | |
| Shipping Date | |
| Order Status |
The Customer ID in the Order table connects each order to the corresponding customer.
¶ 1.1. How the relationship works
Because both tables use the same Customer ID, the system can:
- Show all orders for a customer
- Fetch customer details for any order
- Track order status and delivery delays
- Generate reports using data from both tables
This link keeps data connected without duplication and supports accurate reporting.
¶ 2. Relational databases: A few examples
Relational databases are managed using database systems called RDBMS. These systems are used to create, update, and manage tables, records, and relationships. Common relational database systems include:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- MariaDB
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Oracle Database
These systems all follow the same table-based structure and relationship model.
In Quixy, the database layer is managed by the platform. Tables, relationships, and application data are created and managed through the Quixy interface.
¶ 3. Advantages of Relational Databases
The main benefit of the relational database model is that it makes data easy to understand and makes it easy to get to data points that are related. Relational databases are most often used by organizations that need to manage a lot of structured data. This includes keeping track of inventory, processing transactional data, and logging application data.
Using relational databases to manage and store your data also has a lot of other benefits, such as:
- Flexibility: It's easy to add, update, or delete tables, relationships, and other data at any time without changing the overall structure of the database or affecting applications that are already running.
- ACID compliance: Relational databases use ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) performance to make sure that data is valid even if there are mistakes, failures, or other problems.
- Usage-friendly: SQL makes it easy to run complex queries, so even people who aren't tech-savvy can learn how to use the database.
- Collaboration: Multiple people can operate and access data simultaneously. Data that is being changed can't be accessed at the same time because of built-in locking.
- Built-in Security: Role-based security makes sure that only certain users can access data.
- Database normalization: Relational databases use a method called "normalization" to make sure that data is correct and doesn't repeat itself.
¶ 4. What is ER Diagram? How does it show cases relationship between data tables?
An ER (Entity-Relationship) diagram is a type of data modeling that illustrates the logical structure of databases. It shows the entities (things) in the database and the relationships between them. Here's how it works:
- Entities: Entities are the things or objects in the database that are represented by data tables. For example, in a database for a university, entities could include Student, Course, and Instructor.
- Attributes: Attributes are the properties or characteristics of entities. For example, a student entity might have attributes like Student ID, Name, and Date of Birth.
- Relationships: Relationships describe how entities are related to each other. There are different types of relationships:
- One-to-One: Each entity in the first set is related to exactly one entity in the second set.
- One-to-Many: Each entity in the first set is related to zero or more entities in the second set.
- Many-to-Many: Each entity in the first set is related to zero or more entities in the second set, and each entity in the second set is related to zero or more entities in the first set.
Example
In an ER diagram for a university database, you might have entities like Student, Course, and Instructor. A Student entity could be related to a Course entity through a "Enrolls In" relationship, which could be a One-to-Many relationship (one student enrolls in many courses, but each course is taken by one or more students).