Services in Quixy function similarly to applications but operate as backend mechanisms that support the functionality of Kanban view and for upcoming views such as Map, Calendar etc. A service can be created independently, but it cannot function without being linked to a view. Let’s dive into how services help the views update data points (e.g.: Kanban view).
Service as a function or feature doesn't have any significance of its own, however when it is linked with Kanban view it enhances the core functionality of the Kanban. To explain this further, let’s consider a Customer Support Ticket use case, where the Kanban view is used to track tickets. In this case, the tickets are divided into different stages, like Open, In Progress, Resolved, Hold, and Closed, which represent the progression of the support tickets.
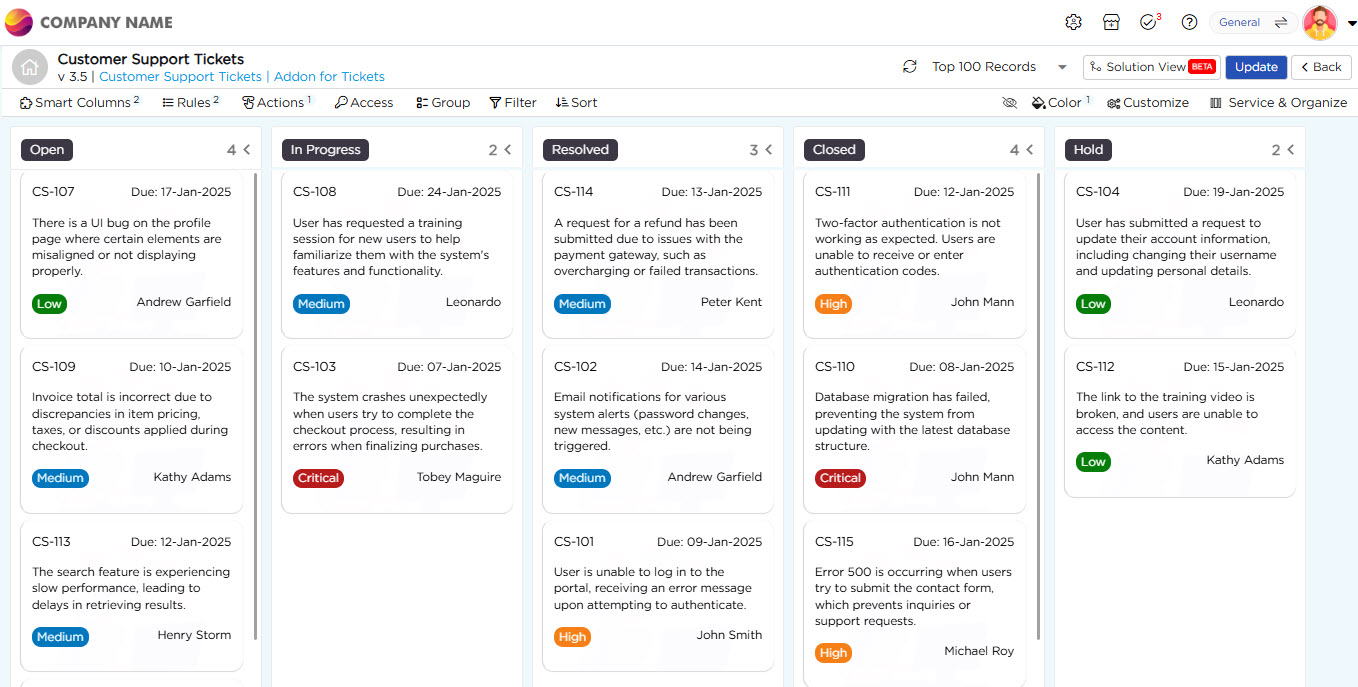
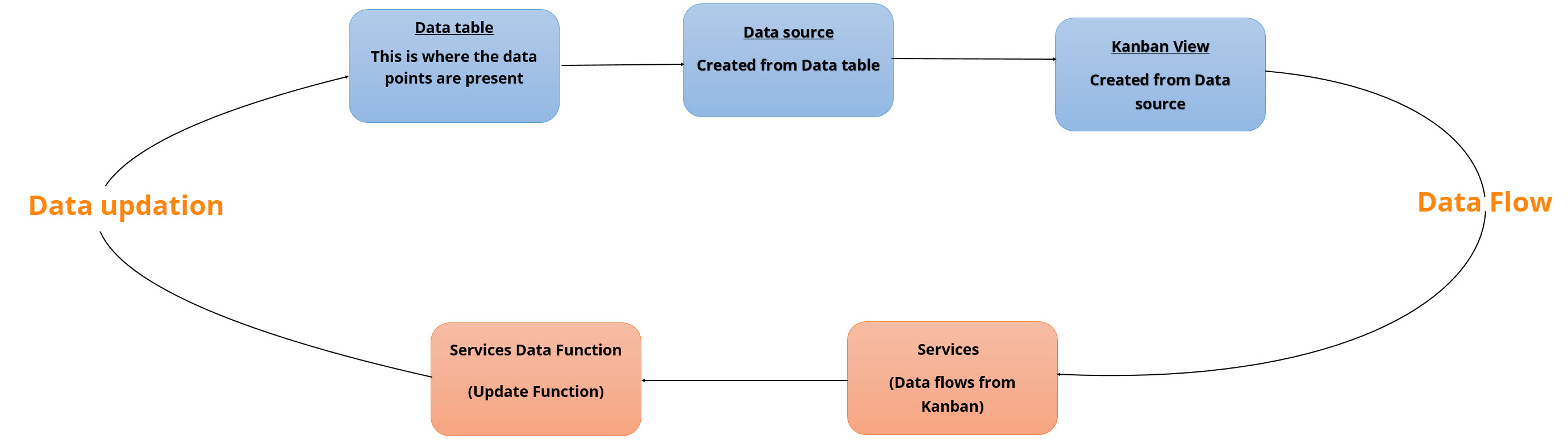
When a card is moved through stages in the Kanban view, the corresponding stage of the particular card needs to be updated in the data table (eventually leading to update in data source and Kanban view). This is where Services come in. Just like applications, services will have elements that capture data, and we need to create services with elements that match those in the Kanban.
Since the service operates as the backend mechanism for the Kanban, the first step is to map the Service elements to the corresponding elements in the data table. This establishes a connection, allowing the service to update the table whenever changes occur. To facilitate this, we create events (data functions) within the service that establish the mapping between the service elements and the data table elements. Once this is set up, the service is then linked to the Kanban by mapping its elements to the Kanban board.
Now, whenever a card moves from one stage to another, the service detects this change and triggers its update function, ensuring the data table reflects the new status. Since the data source is built on the updated table, the Kanban board also stays in sync. This process keeps everything connected and ensures a smooth workflow.
¶ Service Structure
A Service now contains the following sections:
- Elements – Define the fields required for data capture and updates.
- Business Rules – Configure conditions to dynamically set or update values.
- Events – Define data functions such as create, update, or delete.
- End Points – Connect the Service to external systems via webhook APIs.
¶ Creating a Service
- A Service can be either created manually or using a JSON object.
- Let’s now understand how to create a service manually.
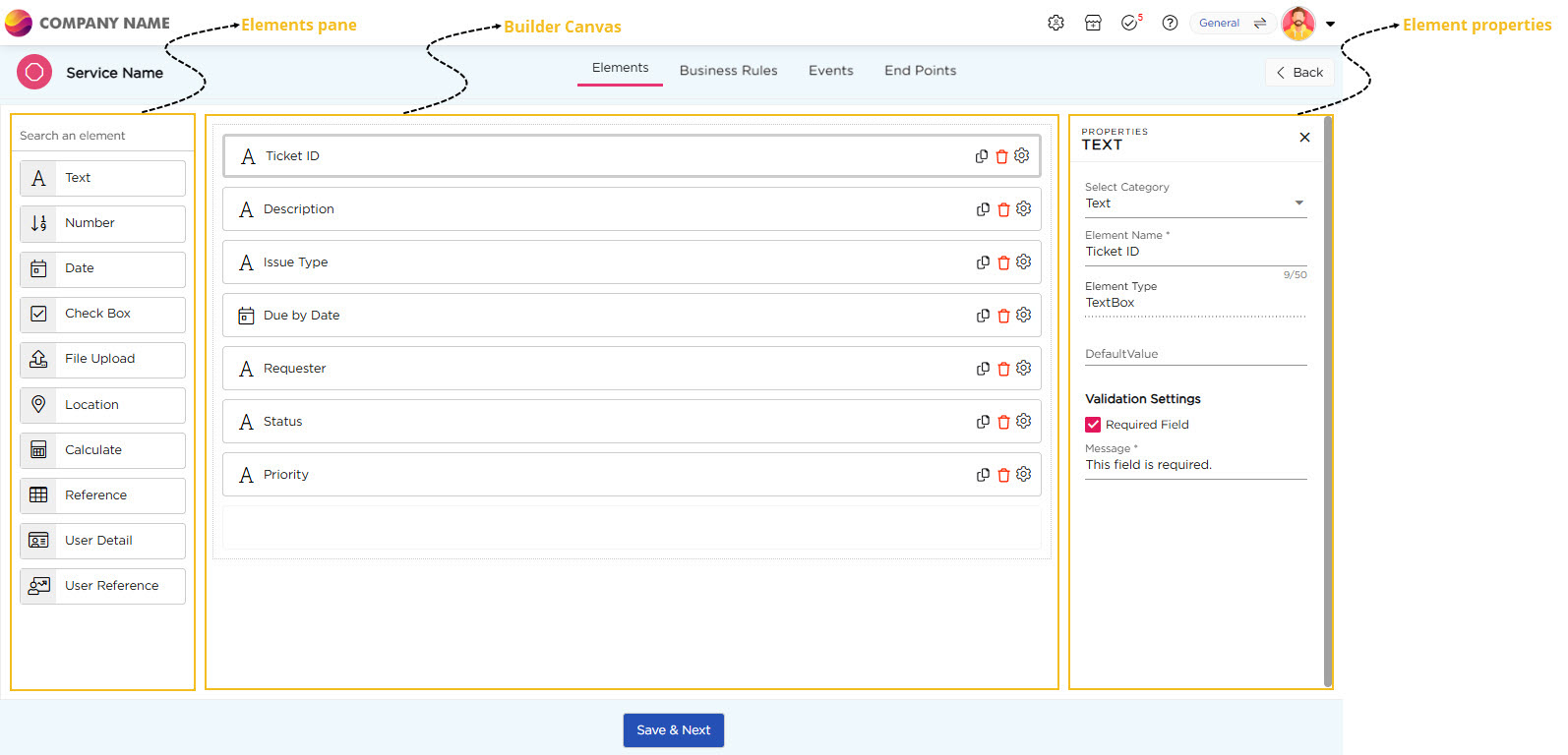
- Go to Admin Menu → Apps → Create Service.
- Select the elements for the Service that correspond to the fields displayed in the Kanban view such as:
- Ticket ID (Text)
- Description (Text)
- Issue Type (Text)
- Due by Date (Date)
- Requester (Text)
- Status (Text)
- Priority (Text)
- Click Save, once you've added all the necessary elements.
¶ Using Business Rules in Services
After configuring elements, you can use the Business Rules tab to set values dynamically based on conditions. Business Rules help automate actions without relying only on events.
For example:
- If a ticket is moved to Resolved, you can automatically update the Status, assign a user, or set a timestamp.
- When a card reaches On Hold, a rule can set a comment or delay field.
This ensures that Services don’t just move data but respond intelligently during stage transitions or updates.
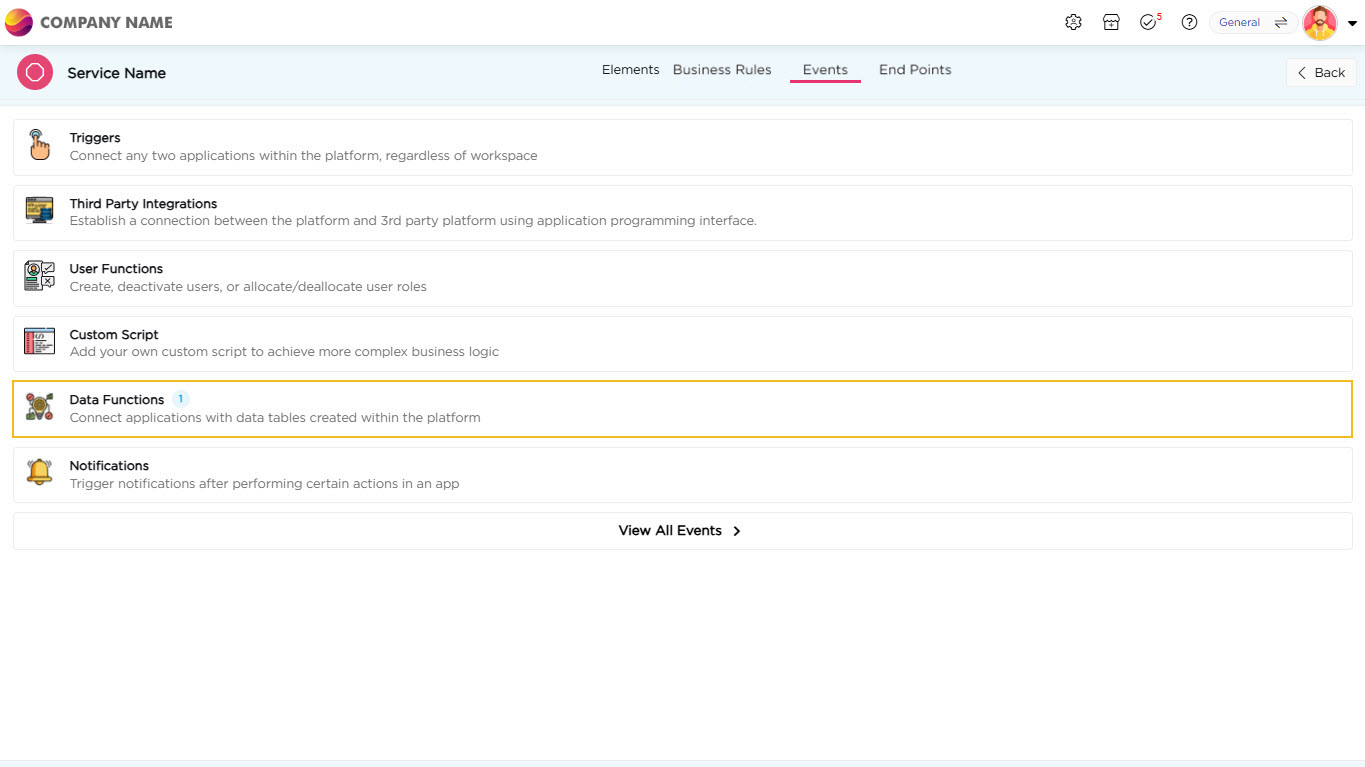
¶ Configuring Events
- Navigate to the Events tab.
- Select Data Functions and click Add.
- Name the event.
- Select the data table used by the Kanban.
- Choose the Update function and click Configure.
- Map Service elements to the data table fields and click Save.
Once saved, the Service logic becomes active.
¶ Using End Points
Under the End Points tab, you can enable webhook integrations if needed to connect the Service with external systems. This is useful when pushing data outside the platform or receiving external triggers.
Once you’ve configured the elements, business rules, events, and endpoints, link the Service to the Kanban view. When you drag a card between stages, the data updates instantly, keeping the Kanban board, data tables, and data sources in sync.
After setup, your Service will manage customer support tickets directly in the Kanban view. For more information, see the Kanban article.