Data Functions serve as a bridge between an Application and a Data Table, creating a relationship between the two. This ensures that any record submitted through the application is directed to and stored in the data table.
There are two types of data functions:
- App Data Functions
- Data Table Functions
In this article, we will discuss about App Data Functions and How to create them
¶ What Are Data Functions in Applications?
Data functions control how data flows between an application and its data table, ensuring seamless interaction. They define how records are created (add), modified (update), or removed (delete) based on specific triggers and workflow steps. These functions play a crucial role in maintaining data accuracy, ensuring that each action performed within the application reflects correctly in the database
¶ Why Do We Have to Create Data Functions in an Application?
Creating data functions allows an application to interact with a data table effectively.
Before setting up a data function in an application, data table functions must be created as a prerequisite. This ensures that the application can map its fields to the corresponding fields in the data table, making data processing smooth and error-free.
¶ Create an App Data Function
- Create and Publish a Form: Begin by designing and publishing the required form in your application.
- Navigate to App Settings: Once the form is published, go to the App Settings.
- Select Events: In the settings menu, locate and click on Events.
- Choose Data Functions: Among the available event types, select Data Functions.
- Create a New Data Function: Click on + Add Data Function to start configuring.
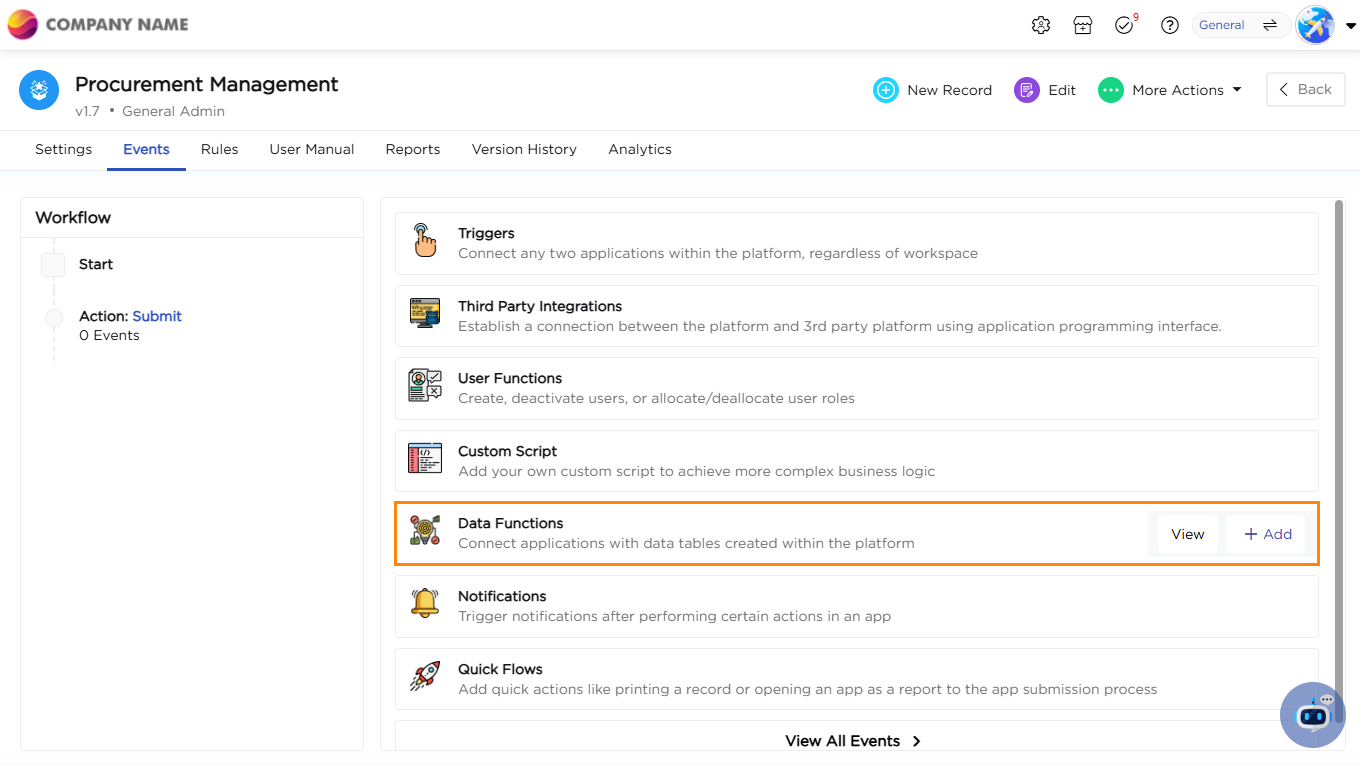
6. Give a unique name to Data Function.
7. Select Workflow steps and step actions.
8. Workflow Steps and Step Action Selection
- Workflow steps define the sequence of actions taken within an application. When configuring a data function, selecting workflow steps and their respective actions ensures that data is stored based on specific actions performed.
- For example, in a leave application workflow:
- Step 1: The employee submits a leave request.
- Step 2: The manager approves or rejects the request.
- Step 3: HR acknowledges the request and updates the records.
9. Choose Single or Multiple Elements.
- Single Element: Used for individual fields (e.g., Name, Contact Number). These fields store one value at a time and do not involve multiple records.
- Multiple Elements (Grid Elements): Used for sub-forms containing multiple fields within a single form. For example, an expense report might have multiple expense entries stored in a grid format.
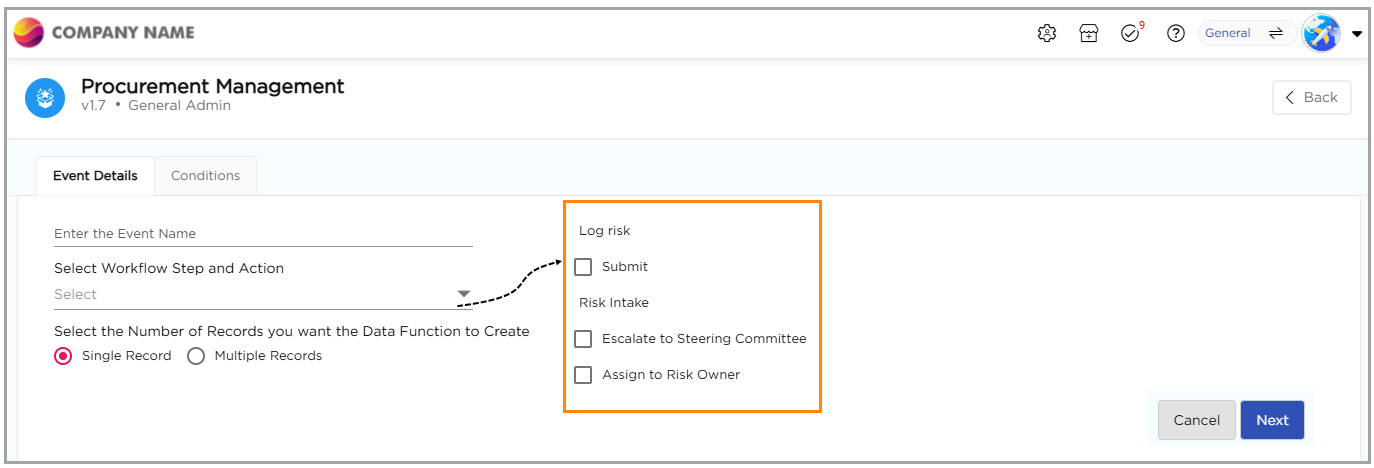
10. Click on Next, where you land on Conditions page.
11. Choose the data table to which you want to map the application. The drop-down will display the list of data tables available within the same workspace as the application.
12. Select the type of function to be performed. Understand the types of functions below.
13. Types of Functions (Add, Delete, Update)
- Add Function: Inserts new records into the data table when a transaction is performed.
- Delete Function: Removes records from the data table based on conditions defined in the workflow.
- Update Function: Modifies existing records in the data table when a workflow step is completed.
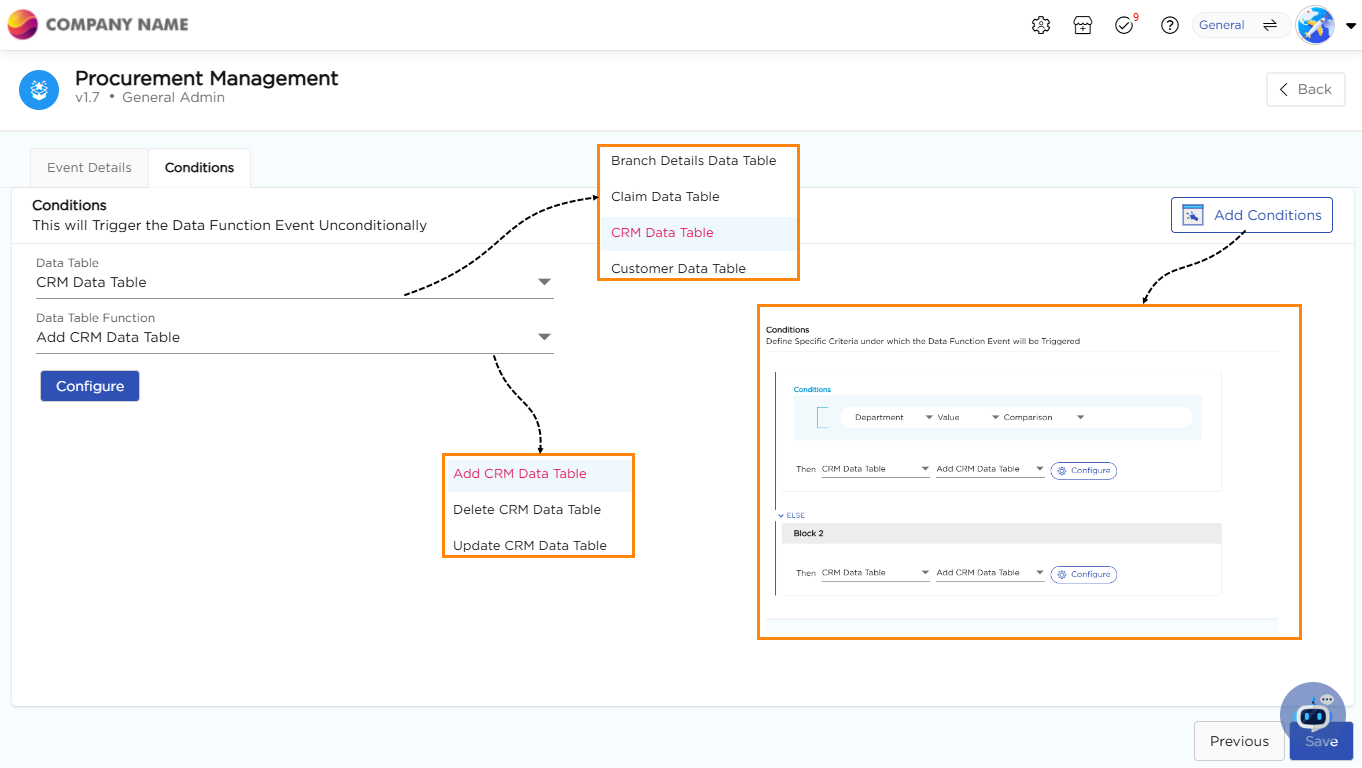
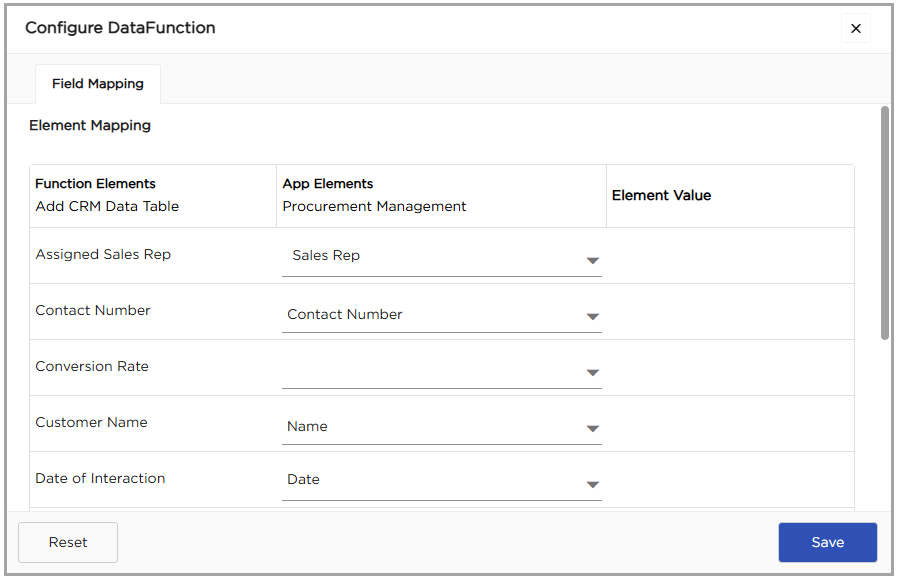
14. Click on configure to map the elements in the application to a data table.
15. Element Mapping: Mapping connects application elements to the corresponding fields in the data table. Proper mapping ensures that data is stored in the right place.
¶ What Are Conditions?
Conditions in data functions act as rules that define where and how data should be stored based on specific criteria. They help filter, direct, or modify data before it gets saved in a data table. By setting conditions, you ensure that only relevant data is stored in the appropriate table, maintaining data accuracy and organization.
Example
In an employee onboarding application, all employee records might be stored in a master employee table. However, employees belong to different departments, and you may need to store department-specific details in separate tables. Conditions help achieve this by applying specific logic:
- Condition: If the employee’s department is “Product,” the record is stored in the Product Employee Table in addition to the master table.
- Condition: If the employee’s department is “Marketing,” the record is stored in the Marketing Employee Table alongside the master table.
These conditions ensure that the data is not only stored in a central repository but also categorized correctly based on business requirements. This improves data retrieval, reporting, and management while preventing unnecessary duplication or misplacement of records.
¶ Finalizing the Data Function
- After configuring all the settings, save the data function.
- Your app data function is now created.
Try creating a data function in your application to understand how it works.